Quck answer
El Niño is a climate phenomenon that occurs in the Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by warmer than usual sea surface temperatures, which can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world. During an El Niño event, the normal trade winds weaken, causing warm water to move from the western Pacific towards the eastern Pacific. This can lead to increased rainfall in the eastern Pacific, droughts in the western Pacific, and changes in atmospheric circulation patterns. El Niño events typically occur every 2 to 7 years and can last for several months to a year.
Are you interested in keeping track of the weather? Or do you rely on others to inform you when to bring a jacket or a raincoat? For those who engage in outdoor activities frequently, monitoring the weather forecast is an essential part of planning. After all, you wouldn’t want to be caught outside without the appropriate clothing and equipment.
We often don’t pay much attention to the weather unless it becomes newsworthy. If you are experiencing a prolonged drought or severe storms are causing chaos in your area, the weather may dominate the headlines. People want to understand why certain weather events occur. Did you know that your local weather can be influenced by events that occur thousands of miles away?
During certain years in the middle of winter, there is a weather phenomenon that you might hear about often: El Niño. But what exactly is El Niño? And how does it impact the weather worldwide?
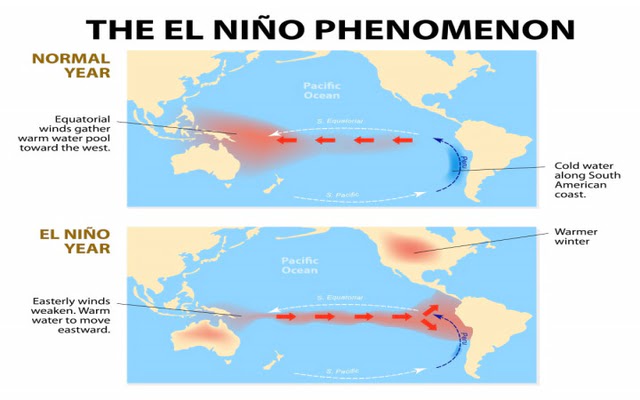
El Niño is a climate cycle in the Pacific Ocean that represents one of the phases of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle. The ENSO cycle involves temperature changes between the ocean and the atmosphere in the eastern Pacific Ocean near the equator.
During an El Niño episode, warm tropical waters in the western Pacific Ocean move eastward along the equator towards the coast of South America. Instead of the warmest waters remaining near Indonesia and the Philippines, these waters sit off the northwestern coast of South America during an El Niño cycle. This is why El Niño is often referred to as the warm phase of ENSO.
If you know Spanish, you may have already deduced that El Niño means “the little boy.” It is also sometimes interpreted as “Christ child,” because Peruvian fishermen who first observed this weather phenomenon back in the 1600s named it El Niño de Navidad. Since El Niño tends to be strongest during December and January, the fishermen gave it a name associated with the Christmas season.
Occasionally, the opposite phenomenon occurs. When trade winds blow warm water even further west than usual, this “cold phase” of ENSO is called La Niña or “the little girl,” indicating that it has the opposite effect of El Niño.
El Niño and La Niña cycles typically last 9-12 months. They are difficult to predict because scientists do not fully understand what causes them to occur. El Niño cycles occur more frequently than La Niña cycles. Scientists estimate that El Niño cycles occur on average every 3-5 years, although they can occur as often as every two years or as rarely as every seven years.
So why does El Niño generate significant news coverage when it happens? Not only does El Niño impact processes in the Pacific Ocean, but it also has a major influence on global weather and climate. Tropical storms shift eastward, affecting both North and South America.
Strong El Niño cycles typically result in above-average precipitation and below-average temperatures during the winter in the southern half of North America, while the northern half of the continent experiences below-average precipitation and above-average temperatures. Northwestern South America often experiences record rainfall during El Niño cycles. Fishing in these areas is also affected as fish migrate to seek colder waters in the north and south.
The impacts of El Niño extend beyond North and South America. Australia and Southeast Asia experience higher temperatures than usual, and these regions often suffer from severe droughts. El Niño-induced droughts can also affect southern Africa and India.
Give it a try
Prepare for bad weather! Gather a few friends or family members to join you in exploring the following activities:
- How’s the weather in your area? If you don’t typically keep track of the weather, start today! Find a local 10-day forecast and write down the weather predictions made by the meteorologist for the next 10 days. Then, observe and record the actual weather during that same time period. Keep a journal noting the daily high and low temperatures, as well as any noteworthy weather events like rainfall, strong winds, etc. How accurate were the meteorologist’s predictions?
- Interested in delving deeper into the phenomenon of El Niño? Create a miniature version! NASA offers instructions and a video tutorial!
- Ready to become a weather scientist? Explore “Investigating El Niño Using Real Data” online, where you can learn more about this weather phenomenon using authentic data. There are various activities tailored to different levels, so choose the one that suits you best!
Recommended Sources
- http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/ninonina.html (accessed October 7, 2022)
- http://www.livescience.com/3650-el-nino.html (accessed October 7, 2022)
- http://www.cnbc.com/2015/05/15/what-is-el-nino-anyway.html (accessed October 7, 2022)
FAQ
1. What is El Niño?
El Niño is a natural climate pattern that occurs when there is a warm phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in the Pacific Ocean. It is characterized by unusually warm ocean temperatures in the central and eastern equatorial Pacific, which can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world.
2. How does El Niño form?
El Niño forms when the normal trade winds weaken or even reverse direction, causing warm water to accumulate in the central and eastern Pacific Ocean. This disrupts the usual patterns of ocean currents and atmospheric circulation, leading to changes in rainfall, temperature, and wind patterns globally.
3. What are the effects of El Niño?
El Niño can have a wide range of effects on weather patterns. It can lead to increased rainfall and flooding in some regions, while causing droughts and reduced rainfall in others. It can also influence the intensity and frequency of tropical storms, as well as alter ocean currents and marine ecosystems.
4. How long does El Niño last?
The duration of an El Niño event can vary, but on average, it typically lasts for about 9-12 months. However, some El Niño events can persist for longer periods, lasting up to two years or more.
5. Can El Niño be predicted?
While it is not possible to predict the exact timing and intensity of an El Niño event with certainty, scientists use various tools and models to monitor oceanic and atmospheric conditions in order to provide early warnings and forecasts. This allows governments and communities to prepare and mitigate the potential impacts of El Niño.





Leave a Reply